Case Study: WhatsApp Automation for Electronics, Mobile & Appliances Industries

Industry Background: Why WhatsApp Automation for Electronics Is Broken
WhatsApp automation for electronics, mobile, and appliance businesses enables brands to turn everyday invoices into lifecycle-driven customer engagement for warranties, service reminders, accessories, upgrades, and payment follow-ups. The operations of electronics and mobile and appliance businesses depend on products which stay in the market for extended periods while customers need frequent maintenance services and the companies must handle numerous customer interactions after sales. The industry achieves value realization through its products which generate ongoing revenue streams starting from the first sale until customers need warranties and accessories and service visits and repairs and AMC plans and product upgrades.
WhatsApp automation for electronics businesses works best when it is triggered by real transactions such as invoices, service records, and warranty documents. Unlike broadcast tools, WhatsApp automation for electronics connects directly to what customers have purchased, serviced, or repaired, making every message contextual and expected.
Most businesses face difficulties when they need to perform operational follow-up work after finishing their transaction. Core challenges include:
- The system lacks a method to monitor when warranties become due for expiration and when customers need to renew their coverage.
- The design fails to provide users with opportunities to attach additional accessories or add-ons.
- Service reminders require manual handling because the system lacks proper consistency in their execution.
- The system requires manual intervention to pursue unpaid service and repair invoices.
- The system lacks any ability to show when upgrades or replacements will occur.
- The system operates WhatsApp as an emergency communication tool instead of using it for business operations.
The required information which appears in invoices and service records exists but remains unorganized and without any application. The system generates reactive customer interactions which staff members must handle while making mistakes that result in lost sales and negative customer service experiences.
Every important customer interaction in electronics and mobile and appliance businesses starts with actual product sales or service delivery instead of marketing activities. The engagement achieves its context-based and time-sensitive and trustworthy nature through this approach.
Why Traditional Tools Fail at WhatsApp Automation for Electronics
Traditional CRMs and broadcast tools fail to support WhatsApp automation for electronics because they do not understand product lifecycles, warranty timelines, or service eligibility. Effective WhatsApp automation for electronics requires invoice-level data to decide who to message, when to message, and why the message is relevant.
Most electronics and appliance businesses operate with a combination of POS systems and CRMs and generic WhatsApp tools. The systems lack ability to support lifecycle-based engagement.
- The POS systems only perform billing functions but they fail to monitor ownership information and warranty details and service schedule deadlines.
- Frontline teams do not update CRMs because these systems need human input for data entry and their information stays outdated.
- The WhatsApp broadcast tools require users to create their contact lists manually without any connection to transaction data.
- The process of service follow-ups depends on staff members remembering information or using paper-based documentation systems.
- The system delivers upgrade and accessory messages to customers who do not possess the required products and whose business stage does not match the product lifecycle.
These tools lack the ability to extract or understand invoice-level data which prevents them from performing automated contextual communication tasks. The practice of engagement results in generic messages which appear at wrong times while failing to connect with actual customer behavior.
Waliner solves this problem through his system which uses invoices and service records to automate operations while removing human involvement for WhatsApp contact management that follows product life cycles.
How the interaction starts
A customer interaction starts when any of these three situations take place:
- Product purchase
The store allows customers to purchase mobile phones and televisions and appliances and accessories at their service counter. The billing process requires the creation of an invoice document. - Service request or repair drop-off
A customer arrives at the store to have their device repaired or installed or for maintenance services. The system generates a job card or service invoice which contains device information along with problem description and projected completion date. - Warranty registration or activation
The customer needs to register their product for warranty after buying it or the retailer will provide a warranty invoice which contains the product serial number and model information and purchase date details.
The system generates service documents which include all necessary information for starting communication after each performed action.
How WhatsApp communication is triggered
The business can distribute customer information to lists and CRM systems through Waliner which supports three different channels for invoice distribution (WhatsApp upload template and chat upload and portal upload).
From that single step:
- The customer needs to use their phone number as their verified communication method.
- The transaction timestamp shows when the interaction took place.
- The context of the interaction (purchase, repair, warranty, unpaid service, etc.) The definition of the problem stands as a clear one.
The system uses this transaction-based event to start WhatsApp communication for sending invoices and service updates and warranty verification without needing human intervention.
How customer and product data becomes available automatically
Once the invoice or service document is uploaded:
- The system extracts customer information which includes their name and phone number before performing normalization on this data.
- The system directly extracts product information which includes brand details and model numbers and SKU codes and serial numbers and category designations from each line item.
- The system transforms transaction context information about payment status and service type and warranty period and repair notes into organized database fields.
The system performs automated extraction and validation to achieve all its operations. The system operates without requiring users to enter data manually while it also eliminates the need for spreadsheet imports and POS and ERP system connections. The invoice serves as the foundation which creates an active customer profile that enables instant communication with customers.
The data connection to real purchase and service activities makes all WhatsApp messages both relevant and expected and fully compliant with regulations. The system sends messages to customers for purchase verification and repair status updates and service payment alerts and accessory suggestions and warranty expiration notifications.

The WhatsApp automation system receives customer and transaction data from electronics and mobile and appliance businesses through their regular business activities instead of requiring dedicated marketing efforts.
How data is captured through simple, existing workflows for WhatsApp Automation for Electronic
Waliner is purpose-built for WhatsApp automation for electronics, mobile, and appliance brands that rely on post-sale engagement. By using invoices as the trigger, WhatsApp automation for electronics becomes an operational system for warranty tracking, service reminders, accessories, upgrades, and unpaid invoice recovery.
The system receives customer and transaction information through existing daily workflows which teams already perform:
- WhatsApp invoice or document uploads
Staff members distribute the invoice or service document to clients through either a WhatsApp upload process or a dedicated portal after the billing process. The single operation enables the system to record all customer information including their phone number and purchase date and all purchased items and payment status and service details. - Billing system outputs (PDFs or receipts)
The invoice data originates from three different sources which include POS systems and desktop billing software and printed receipts that get scanned into PDF format. The system needs no integration or API setup process. - Service and repair records
The process of uploading job cards and service invoices and repair intake forms during device drop-off remains the same because these documents contain device information along with service details and customer identification data..
The system retrieves customer information along with product details and transaction background data from these documents which it then transforms into organized data that can be used.
No new tools for frontline teams
Frontline staff do not need to learn dashboards, CRMs, or campaign tools.
- The company maintains its current billing practices.
- The service records get created through the same process that has been ongoing.
- The system maintains its current method of sending invoices to users.
There is no requirement to:
- Build contact lists
- Tag customers manually
- Export CSV files
- Maintain parallel databases
The automation system adapts to existing workflows instead of forcing teams to change how they work.
Why this approach improves accuracy and speed
Because data is captured now of real customer activity:
- Accuracy is higher — information comes directly from invoices and service records, not manually typed lists.
- Timeliness is immediate — engagement can begin minutes after a purchase, repair intake, or billing event.
- Manual errors are eliminated — no missed numbers, outdated lists, or incorrect customer mapping.
Each WhatsApp message is tied to a verified transaction, ensuring relevance, compliance, and context in every interaction.
WhatsApp automation begins with real customer activity, not assumptions.
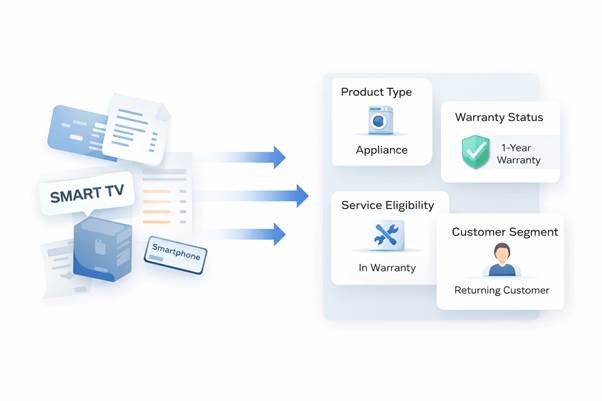
The success of electronics and mobile and appliance businesses depends on their ability to understand customer interactions through analysis of their transaction data which comes from invoices and service records and warranty documents. These documents exist as separate unorganized records which lack any form of organization. The system needs organized decision-ready data to achieve reliable WhatsApp automation operations.
From raw records to structured information
When an invoice or service document is captured, the system first breaks it down into distinct, usable components:
- Customer identity
The system unifies customer information by linking phone numbers to names and purchase records into one customer profile which tracks all customer interactions throughout their multiple visits and service requests. - Product identification
The system analyzes each line item to determine the product category (mobile phone or TV or washing machine or accessory) and extracts brand information and model details and SKU values. The system maintains complete understanding of customer ownership and service history through this process. - Category grouping
The product classification system includes four essential categories which are core device and accessory and consumable and spare part. The system allows proper communication delivery because it separates warranty information from accessory-related messages. - Warranty and lifecycle mapping
The system uses purchase dates to determine when warranties begin and end and to establish eligibility for extended warranties and determine when products need replacement or upgrading. The lifecycle awareness of appliances and electronics requires immediate attention. - Service eligibility and status
Service records show the status of products which includes warranty information and out-of-warranty status and repair status and pickup status and scheduled maintenance requirements. The system blocks any messages which do not match the correct timing or contain unimportant information. - Payment and transaction status
The system identifies invoices through three status labels which indicate whether they have been fully paid or remain partially paid or completely unpaid. The system uses this capability to identify confirmation messages from reminders and escalations without requiring human inspection of each message.
Each of these elements is stored in structured fields rather than free text, making the data immediately usable by automation rules.
Why structured data matters for long product lifecycles
Electronics, mobile devices, and appliances are not short-cycle purchases. Customers interact with these products over months or years—for service, accessories, warranty claims, upgrades, and replacements. Without structured data:
- Warranty reminders may go out too early or too late
- Service messages may reach customers who are no longer eligible
- Upgrade or accessory offers may be irrelevant
- Payment follow-ups may target the wrong customers
The system maintains exact and relevant information about every WhatsApp message which connects to the appropriate product development stage. The system enables automation to detect actual ownership and service status instead of depending on predicted timelines or general assumptions.
The business achieves reliable customer communication through its ability to organize raw invoices and service documents into structured data which includes time-based organization and categorization.
Disorganized data is transformed into actionable WhatsApp intelligence.
The success of WhatsApp automation in electronics and mobile and appliance industries requires systems to identify customer interaction reasons and product status levels instead of tracking basic transaction data. The system achieves this goal through its ability to read customer buying intentions and product life cycle information which it obtains from actual transaction and service records.
Understanding customer intent from real actions
Customer intent is inferred from what the customer does, not from assumptions or generic segments:
- A mobile purchase signals ownership initiation and near-term accessory needs
- An appliance installation or service request signals usage phase and upcoming maintenance requirements
- A warranty registration or repair visit signals concern for protection, reliability, or longevity
Each invoice, service record, or warranty document provides context about why the customer is interacting with the business at that moment.
Mapping products to their lifecycle paths
Once intent is identified, the system places the product into its expected lifecycle:
- Mobile devices
The purchase of a phone through a phone transaction starts a sequence of events which includes buying additional items such as cases and chargers and screen guards and obtaining software assistance and following product update schedules and having the option to exchange the device. The communication process starts by verifying system installation before moving on to suggest additional equipment and end with notifications about upcoming system updates. - Appliances
Washing machines and refrigerators and air conditioners operate for extended periods before needing replacement. The system monitors all purchase activities after acquisition by tracking both installation processes and warranty protection and service requirements and AMC (Annual Maintenance Contract) plan eligibility. The communication focus moves from tracking delivery and installation progress to sending customers service alerts about upcoming maintenance periods and renewal notifications. - Consumer electronics
The warranty duration of televisions and audio systems determines when customers can purchase these products and which additional features they can obtain. The system detects when products reach their warranty expiration date and when extended warranty promotions become applicable and when customers need additional products or product enhancements.
Lifecycle awareness over one-time messaging
Instead of sending isolated messages, the system maintains a continuous understanding of ownership:
- Messages are sent based on where the customer is in the product’s lifecycle
- Offers are timed to relevance, not marketing calendars
- Service and warranty communication respects eligibility and status
- Customers are not repeatedly asked to buy what they already own or don’t need
The lifecycle-based method makes WhatsApp communication appear useful and natural to users instead of being annoying or advertising-like.
The system connects customer intent data to product development schedules to view each customer interaction as a continuous relationship instead of a standalone sale.
The company analyzes every customer contact by studying its complete sequence of events.
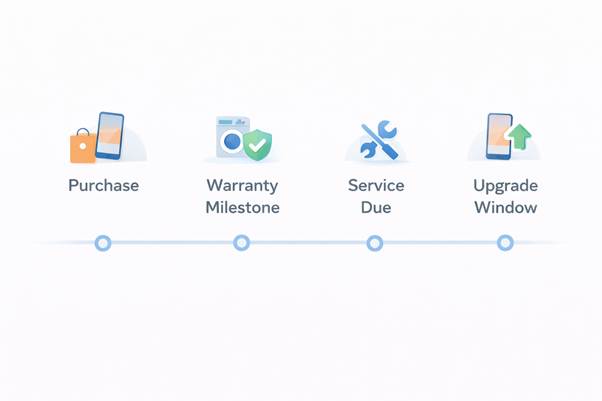
The most effective WhatsApp automation occurs through individual customer timelines which create unique engagement plans instead of sending universal one-time messages to all customers. The timeline unites customer actions with product development stages and all recorded transactions to show essential events in chronological order.
How customers are placed on an engagement timeline
The system creates an initial point on the customer timeline whenever they make a purchase or receive a service. The team will schedule future communication through expected needs and lifecycle milestones instead of running unnecessary campaigns.
The system maintains a flexible timeline which updates itself whenever any new business activity takes place including service visits and repeat purchases and payment changes.
Key timing points in the timeline
Different stages trigger different types of communication:
- Post-purchase
The system provides customers with immediate purchase confirmation along with invoice sharing and setup instructions and warranty registration options after their purchase. The process builds trust between parties which leads to the completion of the transaction process. - Mid-warranty or ownership phase
The system detects mid-warranty periods to provide customers with useful information about product usage and accessory suggestions and warranty extension options at appropriate times. - Service due or maintenance window
The system generates service reminders for appliances and long-life electronics through analysis of usage data and warranty information and AMC program requirements. The messages appear at times when customers need assistance but not before the scheduled time has passed. - Upgrade or replacement eligibility
The system moves product timelines toward replacement or exchange or upgrade options which match standard ownership periods of products near their expiration date.
How customer and product factors influence timing
The system does not treat all customers or products equally. Timing is adjusted using:
- Customer value – High-value or repeat customers may receive earlier or more personalized communication
- Purchase frequency – Frequent buyers move faster through engagement stages than one-time purchasers
- Product type – A smartphone follows a much shorter lifecycle than a refrigerator or washing machine
The system maintains a natural and appropriate communication rhythm through these elements which prevent it from becoming either too frequent or annoying.
The personalized timeline approach for WhatsApp automation enables support functions which do not disrupt customer interactions by delivering messages at their current ownership stage.
Messages are sent when they are most useful, not when they are convenient.
The process of WhatsApp automation requires more than just message content because it needs to determine both timing and delivery frequency and message order. The process at this stage involves controlling the speed of communication while maintaining its importance to deliver messages when customers are ready to receive them instead of following system schedules or marketing deadlines.
How the system decides the right moment to communicate
Every message is triggered by a time-aware decision engine that evaluates whether communication should happen immediately or be delayed.
- Immediate communication is used for high-clarity, expectation-setting moments—such as purchase confirmations, invoice sharing, or service intake acknowledgements.
- Delayed communication is used when value increases with time—such as accessory recommendations, service reminders, or upgrade prompts.
The system asks a simple question before every send: Is this message useful right now, or will it be more useful later?
How message spacing prevents fatigue
Rather than treating WhatsApp as a broadcast channel, the system enforces message spacing rules:
- Minimum gaps between non-urgent messages
- Automatic suppression if a customer has recently received communication
- Cancellation or rescheduling if a newer, more relevant event occurs
This prevents stacking messages too closely together and ensures customers don’t feel overwhelmed or spammed.
Utility messages always come first
Messages are ranked by priority, not by campaign type:
- Utility messages (invoice, payment status, service updates, warranty confirmations)
- Lifecycle messages (service due, warranty expiry, AMC eligibility)
- Promotional or upsell messages (accessories, upgrades, add-ons)
If multiple messages are eligible at the same time, the system sends only the highest-priority message and delays or suppresses the rest.
Timing adjusts based on customer value and behavior
Message cadence is not fixed—it adapts based on:
- Customer value: High-value customers receive fewer, more precise messages
- Engagement history: Customers who read or respond quickly may receive earlier follow-ups
- Purchase frequency: Repeat buyers progress faster through timelines than one-time purchasers
This ensures that active, valuable customers are respected, not over-targeted.
Practical timing examples
- Post-purchase vs accessory recommendation
The system sends both the invoice and confirmation documents to customers right after they make their purchase. The company will postpone accessory recommendations until the customer begins using their purchased product. - Service reminders
The system sends reminders at times which approach the service due date instead of sending messages right away after purchase because this timing matches when customers need to act. - Upgrade communication
The system will only process upgrade or exchange requests after it verifies that the user has proper ownership and has used the product for an adequate period to prevent sending unnecessary messages. - High-value customer pacing
The messaging system sends fewer messages to loyal customers who spend more but each message they receive matches their current stage and purchase intentions.
The purpose of this stage does not involve product comprehension because that process took place during previous steps. The system requires staff to respect customer time while using WhatsApp for communication which should deliver immediate value to customers.
Messages are sent when they are most useful, not when they are convenient.
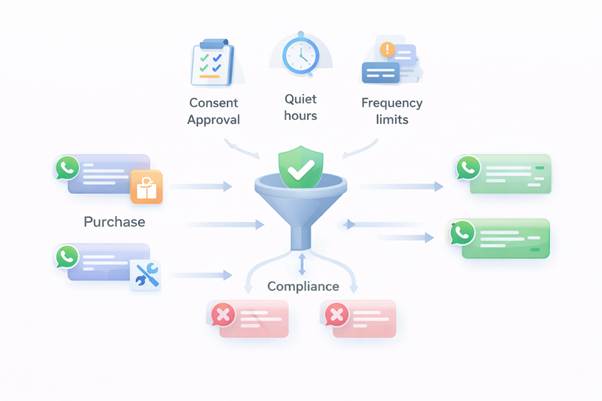
The system performs a thorough eligibility assessment and compliance verification before allowing any WhatsApp message to be sent for determining the right time to communicate. The process serves as a protective measure which confirms messages reach customers at proper times while following established rules and maintaining their privacy..
How message eligibility is determined
Every potential message pass through a decision layer that answers a simple question: Should this message be sent right now to this customer?
To do that, the system evaluates multiple conditions together, not in isolation.
Consent and opt-in validation
The first and most critical check is customer consent.
- The system verifies that the customer has opted in to receive WhatsApp communication.
- Opt-out signals are respected immediately, with no further messages sent unless consent is re-established.
- Consent status is checked for every proactive message, not just once.
This ensures communication is permission-based and expected.
Quiet hours and time-of-day controls
Even valid messages are suppressed if they fall outside allowed time windows.
- Messages are blocked during configured quiet hours based on the customer’s local time.
- Utility messages may be delayed rather than dropped, ensuring they are delivered at the next appropriate time.
- Promotional messages are never forced through restricted periods.
This prevents disruption and maintains a respectful customer experience.
Frequency limits to prevent fatigue
The system enforces frequency caps to avoid over-messaging.
- Limits are applied across message types and time periods.
- If a customer has recently received communication, lower-priority messages are postponed or cancelled.
- New events can replace older, less relevant messages to avoid stacking.
This keeps WhatsApp communication light, intentional, and non-intrusive.
Priority between utility and promotional messages
Not all messages are treated equally. The system uses a priority hierarchy:
- Utility messages – invoices, payment status, service updates, warranty confirmations
- Lifecycle messages – service due, warranty expiry, eligibility notifications
- Promotional messages – accessories, upgrades, add-ons, offers
If multiple messages qualify at the same time, only the highest-priority message is sent. Lower-priority messages are delayed or suppressed entirely.
Why compliance protects trust and brand reputation
By enforcing these checks automatically:
- Customers receive only messages that are relevant and expected
- Brands avoid policy violations and account risk
- WhatsApp remains a trusted service channel, not a marketing spam channel
- Long-term engagement quality improves instead of degrading over time
Compliance is not a restriction—it is what enables sustainable, high-quality customer communication.
Only relevant, compliant messages reach the customer.
The delivery of WhatsApp messages occurs through automated processes which start from actual customer activities and their life cycle stages. The system creates a sequence of natural customer interactions which follow their needs and operational stages instead of delivering separate messages.
How automated journeys work
The automated process starts when a system detects a qualifying event which includes both purchase activities and service intake and payment status changes and warranty milestone achievements. The system starts running messages through an automated process which performs scheduling and adjustment and cancellation based on customer behavior and their qualification status.
Each journey follows a clear logic:
- Start from a real transaction or service event
- Deliver messages in a defined order
- Pause, advance, or stop based on customer response or status updates
This ensures WhatsApp communication feels continuous and purposeful, not fragmented.
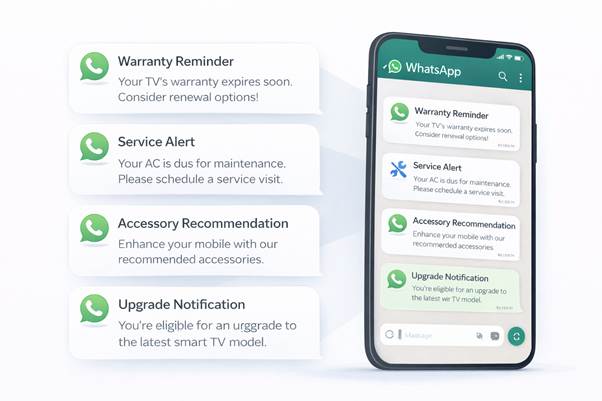
Types of messages delivered in journeys
Different message types are used depending on where the customer is in their lifecycle:
- Warranty reminders
Sent before warranty expiration or eligibility milestones, helping customers take timely action without manual follow-up. - Service updates
Used for repair intake confirmations, ready-for-pickup notifications, or scheduled maintenance reminders—keeping customers informed throughout service workflows. - Accessory recommendations
Triggered after a suitable usage period, based on the product owned. These messages are contextual add-ons, not generic promotions. - Upgrade alerts
Delivered only after sufficient ownership time has passed, aligned with typical replacement or upgrade cycles for the product category. - Payment reminders
Automatically sent for unpaid or partially paid invoices, escalating gently and stopping immediately once payment is completed.
Each message is tied to a specific operational need, not a broadcast campaign.
WhatsApp as an operations-first channel
In this model, WhatsApp is treated primarily as a service and operations channel:
- Customers expect updates and reminders there
- Messages are contextual, timely, and transactional
- Communication supports service delivery, payments, warranties, and ownership management
Marketing-style blasts are avoided. The platform now delivers precise helpful content about existing products and requested services to customers through WhatsApp.
Businesses can replace their current manual follow-up process with dependable system-driven communication which customers trust through WhatsApp integration into their automated journeys.
WhatsApp becomes a reliable operational communication channel.
Performance tracking enables WhatsApp automation to evolve from a fixed workflow into an ongoing system improvement process. The platform receives feedback from all messages which users send and receive and perform actions to enhance upcoming communication through improved timing and increased accuracy and better content matching.
How WhatsApp automation performance is measured
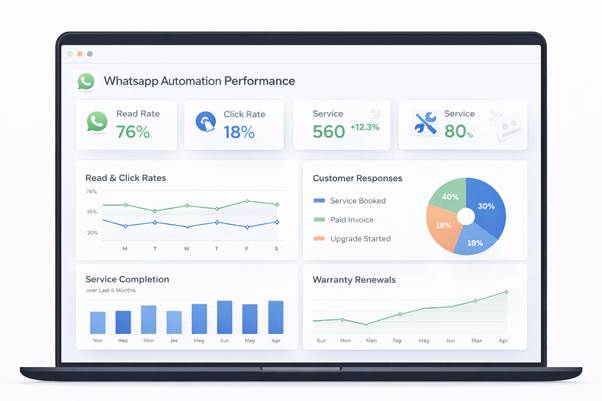
Each automated journey is instrumented with event-level tracking that follows what happens after a message is delivered. Instead of only measuring sends, the system observes how customers engage and act.
Key performance signals include:
- Read rates
Confirms whether messages are being opened, indicating timing and relevance. - Click rates
Tracks interactions with links such as service booking, warranty renewal, accessory pages, or payment links. - Service completion
Measures whether service reminders result in actual service visits, repairs, or AMC activations. - Warranty renewals and extensions
Tracks conversions from warranty reminder messages to successful renewals or add-on purchases. - Follow-up actions
Captures downstream outcomes such as replies, payments completed, accessories purchased, or upgrades initiated.
These signals are tied back to the original trigger, message type, timing, and customer segment.
Turning insights into optimization
Performance data is not only reported—it is actively used to improve future journeys:
- Timing optimization
If messages are consistently read later or ignored, delivery windows are adjusted to better match customer behavior. - Message prioritization
Message types that drive action are promoted, while low-performing messages are delayed, refined, or suppressed. - Journey refinement
If customers complete actions early, later reminders are automatically cancelled. If action is delayed, follow-ups are adjusted. - Segment-level learning
High-value or high-engagement customers are treated differently from low-engagement ones, improving relevance without increasing volume.
Over time, the system learns which messages work best for which customers, at which stage, and under which conditions.
Why performance tracking matters
Without performance tracking, WhatsApp automation becomes guesswork. With it:
- Messaging becomes progressively more accurate
- Customer fatigue is reduced
- Operational outcomes improve
- Business teams gain visibility into what drives results
Every message contributes to a feedback loop that strengthens the entire communication strategy.
Every interaction improves the next WhatsApp journey.
Impact & Measurable Outcomes
After implementing invoice-driven WhatsApp automation, electronics, mobile, and appliance businesses observe clear operational and revenue improvements:
- Higher warranty renewals due to timely, contextual expiry reminders
- Improved service completion rates with automated service due and pickup notifications
- Increased accessory attachment through lifecycle-based recommendations
- Faster unpaid invoice recovery via automated payment reminder journeys
- Reduced frontline workload by eliminating manual follow-ups and list preparation
- Improved customer trust through relevant, expected WhatsApp communication
The system verifies all messages through transaction or service event records which results in better engagement quality without producing more messages. The system develops self-optimizing engagement capabilities through performance insights which improve its ability to optimize timing and pacing and journey logic.
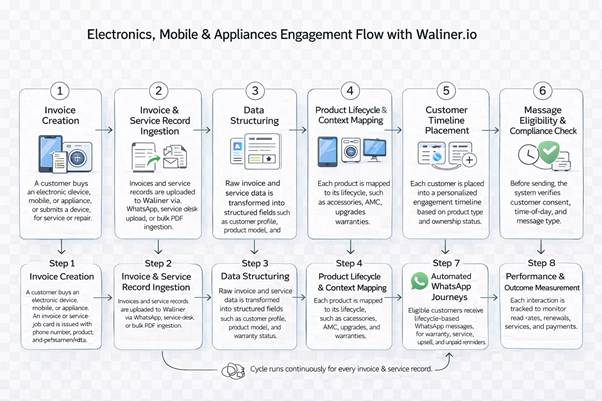
ELECTRONICS, MOBILE & APPLIANCES ENGAGEMENT FLOW WITH WALINER.IO
Step 1 — Invoice Creation
What happens
A customer purchases a mobile phone, electronic device, or appliance, or submits a device for service or repair.
An invoice or service job card is generated containing:
- Customer phone number
- Product model, brand, serial number
- Purchase or service date
- Warranty and payment details
Why it matters
This transaction marks the start of the customer lifecycle, not a marketing campaign.
Step 2 — Invoice & Service Record Ingestion
What happens
Invoices and service records are shared with Waliner via:
- WhatsApp invoice upload
- Service desk document upload
- Bulk invoice PDFs
Why it matters
Staff continue using existing billing and service workflows—no CRM updates, no manual lists.
Step 3 — Data Structuring
What happens
Raw invoice and service data is automatically converted into structured fields:
- Customer identity (phone-based profile)
- Product details (category, model, serial)
- Transaction context (purchase, repair, unpaid, warranty)
Why it matters
Unstructured documents become usable data for automation.
Step 4 — Product Lifecycle & Context Mapping
What happens
Each product is mapped to its lifecycle path:
- Mobiles → accessories, protection, upgrades
- Appliances → installation, service schedules, AMC
- Electronics → warranty, add-ons, replacement cycles
Why it matters
The system understands what the customer owns and what comes next.
Step 5 — Customer Timeline Placement
What happens
The customer is placed into a personalized engagement timeline based on:
- Product type and expected lifespan
- Purchase value and frequency
- New vs repeat ownership
Examples:
- Immediate: invoice + warranty confirmation
- Delayed: accessory or AMC suggestion
- Later: upgrade or replacement window
Why it matters
Messages are timed to usefulness, not urgency.
Step 6 — Message Eligibility & Compliance Check
What happens
Before sending any WhatsApp message, the system verifies:
- Customer consent and opt-in status
- Quiet hours and frequency limits
- Utility vs promotional priority
Only compliant messages proceed.
Why it matters
Protects customer trust and WhatsApp account health.
Step 7 — Automated WhatsApp Journeys
What happens
Customers receive lifecycle-based WhatsApp messages such as:
- Warranty registration & expiry reminders
- Service status and ready-for-pickup alerts
- Accessory recommendations
- AMC or extended warranty offers
- Upgrade eligibility notifications
- Unpaid service or repair reminders
Why it matters
WhatsApp becomes a service and operations channel, not a broadcast tool.
Step 8 — Performance & Outcome Measurement
What happens
Every interaction is tracked:
- Read and click rates
- Service completion
- Warranty renewals
- Payments and upgrades
Insights continuously refine timing and messaging.
Why it matters
Each interaction improves the next customer journey.
Continuous Loop
Every new purchase, service visit, or repair re-enters the same system:
- Profiles are updated
- Lifecycles advance
- Journeys adjust automatically
The cycle runs continuously for every invoice and service record.





Review Case Study: WhatsApp Automation for Electronics, Mobile & Appliances Industries.